In this tutorial I will show you how to identify and fix some of the frequently recurring formula errors in Excel.
#### Error
The #### Error code is displayed when your column is not wide enough for Excel to display the value in the cell.
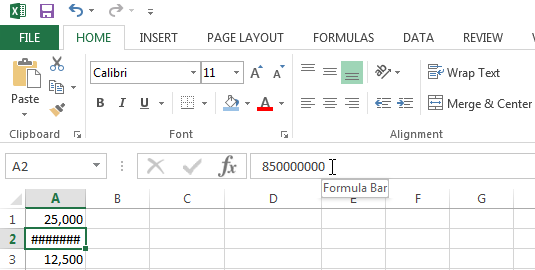
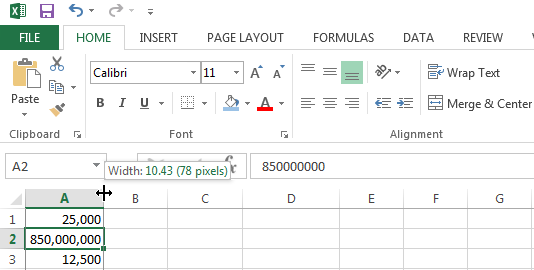
To fix this error code click on the right border of the column header and increase the column width. You can also have Excel automatically adjust the column width so the widest cell in the column fits. To do this simply double click on the right-side of the column border.
#NAME? Error
The #NAME? code is displayed when Excel does not recognize text in one of your formulas.
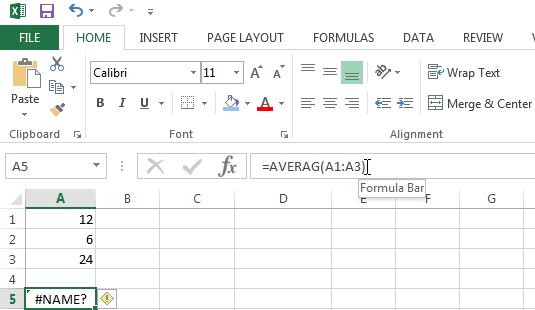
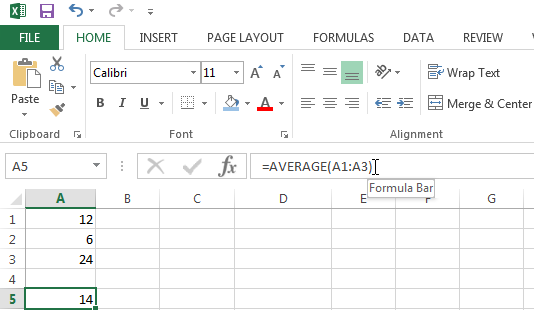
In the example below I incorrectly wrote the AVERAGE function.
#Value! Error
The #VALUE! code is displayed when you inserted the wrong type of argument in your formula.
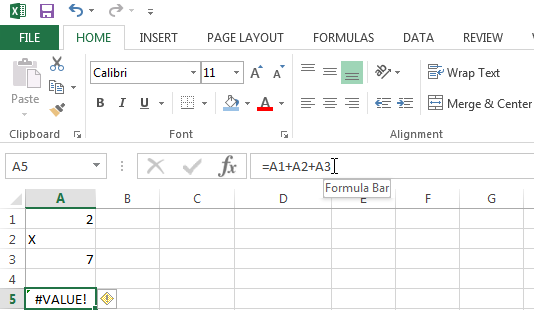
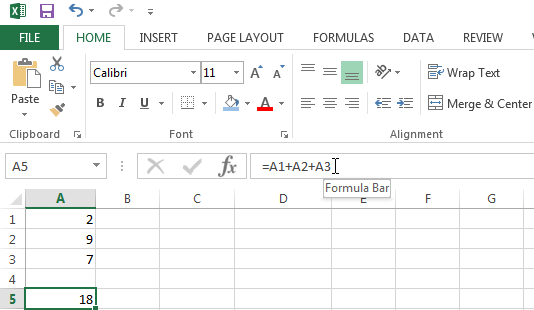
In the example below there is text instead of a number in cell A2. All I have to do to resolve this is to change the value in cell A2 to a number or to use a function to ignore cells containing text.
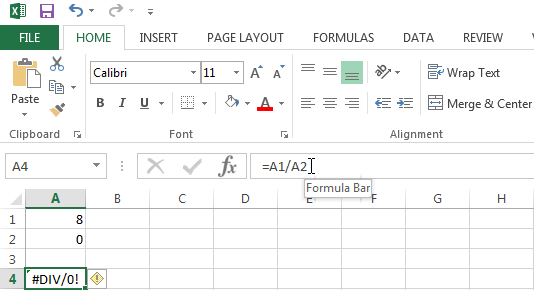
#DIV/0! Error
The #Div/0 code is displayed when a formula in Excel attempts to divide a number by 0 or an empty cell.
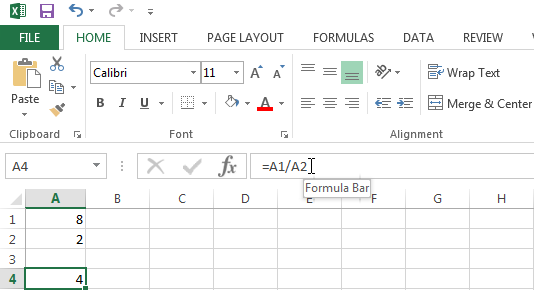
To fix this error either change the value of the cell containing the 0 or stop the error from being displayed by using the IF function as shown below.
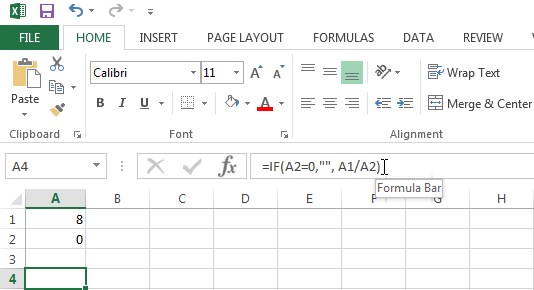
Explanation: If cell A2 equals 0, an empty string is displayed. If not, the result of the formula A1/A2 is displayed.
#REF! Error
Excel displays the #REF! error when a formula refers to a cell that is not valid.
The formula in cell C3 refers to cells A1 and B1.
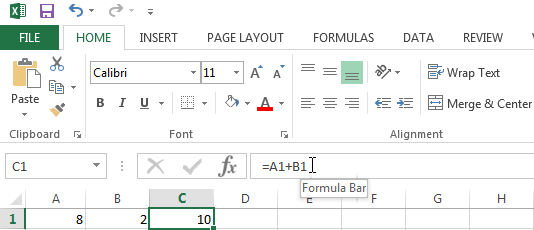
If you were to (accidentally) delete column B for example, then your function in cell C1 would shift over to cell B1 and your function would no longer be valid.
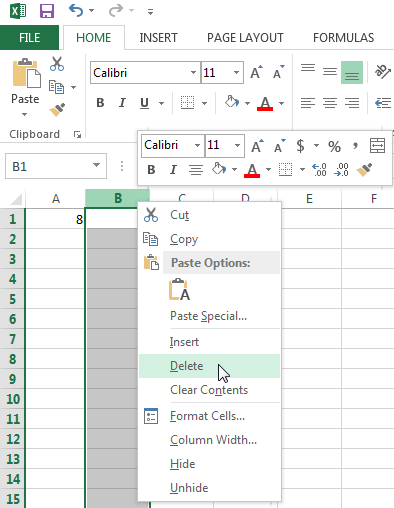
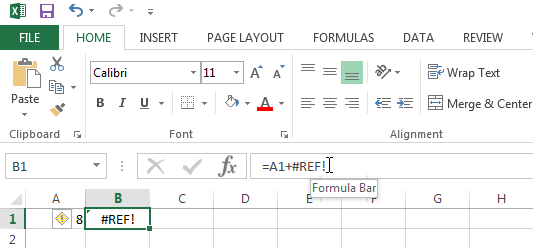
To fix this error you can click on Undo in the Quick Access Toolbar (CTRL + Z), or delete the +#REF! in the formula. Note that when clicking Undo Excel will revert your previous action, in this case deleting column B.
If you encountered any errors while following this tutorial, let me know below and I’ll help you.

Speak Your Mind